1994 Economics WAEC SSCE (School Candidates) May/June: Difference between revisions
From WikiQuestions
(Economics 1994) |
(inserted images) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
=== Economics 1 - Objective === | === Economics 1 - Objective === | ||
<ol> | <ol> | ||
<li> | <li>The definition of Economics as 'the science which studies human behaviour as a relationship between ends and scarce means which have alternative uses' was given by | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>Adam Smith</li> | ||
<li> | <li>David Ricardo</li> | ||
<li> | <li>Lionel Robbins</li> | ||
<li> | <li>Thomas R. Malthus</li> | ||
<li>Robert Giffen</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>The concept of economic efficiency primarily implies | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>obtaining the maximum output from available resources at the lowest possible cost</li> | ||
<li> | <li>conserving our petroleum resources</li> | ||
<li> | <li>equity in the distribution of the nation's wealth</li> | ||
<li> | <li>producing without waste</li> | ||
<li>the limited wants-unlimited resources dilemma</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Which of the following is true of NEPA as a public corporation in Nigeria? It is | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>a solar energy distributor</li> | ||
<li> | <li>organized in a perfectly competitive market</li> | ||
<li> | <li>a duopoly</li> | ||
<li> | <li>a monopolistically competitive industry</li> | ||
<li>a monopoly</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>A situation of full employment exists when | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>every adult is employed</li> | ||
<li> | <li>all adults who can work are employed</li> | ||
<li> | <li>all persons who have attained the age of 15 years and above are employed</li> | ||
<li> | <li>only the disabled are not employed</li> | ||
<li>all those who are able and eligible to work are employed</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Which of the following functions of money makes it possible for any person to provide for old age | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>Medium of exchange</li> | ||
<li> | <li>Store of value</li> | ||
<li> | <li>Measure of value</li> | ||
<li> | <li>Unit of account</li> | ||
<li>Standard for deferred payments</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>The primary objective of the Agricultural Credit Guarantee Scheme is the provision of | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>guarantee for loans granted by banks for agricultural purposes</li> | ||
<li> | <li>agricultural inputs to facilitate credit from banks</li> | ||
<li> | <li>loans for every farmer</li> | ||
<li> | <li>agricultural products for farmers</li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Which of the following is not an advantage of localization of industries? | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>Enjoyment of external economies</li> | ||
<li> | <li>Development of subsidiary industries</li> | ||
<li> | <li>Development of organized markets</li> | ||
<li> | <li>Growth of conurbation</li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Which of the following is not an advantage of government ownership of enterprises? | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>More capital is provided</li> | ||
<li> | <li>Pricing policy may be in the interest of consumers</li> | ||
<li> | <li>Government workers may be indifferent towards the public</li> | ||
<li> | <li>Infrastructures are rapidly developed</li> | ||
<li>Income may be more evenly distributed</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>If the foreign exchange rate is N8 to £1, then a bicycle bought for £40 will cost | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>N15.00</li> | ||
<li> | <li>N60.00</li> | ||
<li> | <li>N100.00</li> | ||
<li> | <li>N250.00</li> | ||
<li>N320.00</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>All the following are assets of a commercial bank except | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>cash</li> | ||
<li> | <li>bills discounted</li> | ||
<li> | <li>bank deposits</li> | ||
<li> | <li>investment</li> | ||
<li>advances to customers</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>The Central Bank controls commercial banks through all the following measures except | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>the use of directives</li> | ||
<li> | <li>the use of bank rate</li> | ||
<li> | <li>Open market operations</li> | ||
<li> | <li>accepting deposits</li> | ||
<li>demanding special deposits</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>If a person supplements his current income by drawing on past savings in order to make both ends meet, he is said to be living | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>a good life</li> | ||
<li> | <li>an average life</li> | ||
<li> | <li>on his savings</li> | ||
<li> | <li>a reckless life</li> | ||
<li>on borrowed money</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Which of the following is not a set of measures of central tendency? | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>Mode and median</li> | ||
<li> | <li>Mean and median</li> | ||
<li> | <li>Mean and mode</li> | ||
<li> | <li>Median and percentage</li> | ||
<li>Mode, mean and median</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>The diagram here is a <br /> [[File:Economics 1994 pie chart.png|alt=Pie chart|thumb|Pie chart|none|277x277px]] | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>bar chart</li> | ||
<li> | <li>pie chart</li> | ||
<li> | <li>ball chart</li> | ||
<li> | <li>histogram</li> | ||
<li>histo-chart</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Which of the following pairs can be referred to as middlemen? | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>Wholesalers and agents</li> | ||
<li> | <li>Retailers and consumers</li> | ||
<li> | <li>Consumers and agents</li> | ||
<li> | <li>Wholesalers and retailers</li> | ||
<li>Wholesalers and consumers</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Mono-product economies are those that | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>have a rich cultural heritage</li> | ||
<li> | <li>produce only raw materials</li> | ||
<li> | <li>live on the exportation of their raw products</li> | ||
<li> | <li>produce one main commodity</li> | ||
<li>specialize in agricultural industries</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>In diagram below, the broken line labelled PM is the Marginal Revenue Curve of a <br /> [[File:Screenshot 2025-05-08 175225.png|alt=Economics 1994 graph|thumb|Economics 1994 graph]] | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>monopoly</li> | ||
<li> | <li>competitive firm</li> | ||
<li> | <li>state corporation</li> | ||
<li> | <li>partnership</li> | ||
<li>monopsony</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>A Nigerian household's demand curve for semovita is downward sloping because | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>the demand for semovita is high</li> | ||
<li> | <li>the local markets are flooded with semovita</li> | ||
<li> | <li>semovita is produced in Nigeria</li> | ||
<li> | <li>every household can afford to buy semovita</li> | ||
<li>the higher the price of semovita, the lower the quantity demanded</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>To the economist, a stock of goods existing at a particular time and conforming to certain requirements such as having utility, money value and being limited in supply, is known as | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>consumer goods</li> | ||
<li> | <li>products</li> | ||
<li> | <li>wealth</li> | ||
<li> | <li>commercial goods</li> | ||
<li>durable goods</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>The decision to consume more of one product will under normal circumstance imply that | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>more of another product will be consumed</li> | ||
<li> | <li>less of something else will be consumed</li> | ||
<li> | <li>no other product will be consumed</li> | ||
<li> | <li>decision-making is basic in Economics</li> | ||
<li>enough resources are available</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>The difference between the Gross Domestic Product(GDP) and the Gross National Product (GNP) is the | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>allowance for total depreciation</li> | ||
<li> | <li>total interest payment</li> | ||
<li> | <li>net income from abroad</li> | ||
<li> | <li>total tax and interest payments</li> | ||
<li>net internally generated income</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>One of the functions of a commercial bank is that it | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>is responsible for formulating monetary policies</li> | ||
<li> | <li>accepts demand and time deposits from customers</li> | ||
<li> | <li>is the lender of last resort</li> | ||
<li> | <li>is the banker of the government</li> | ||
<li>is responsible for issuing currency notes</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Which of the following is not a problem of distribution of goods in Nigeria? | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>Poor communication network</li> | ||
<li> | <li>Inadequate storage facilities</li> | ||
<li> | <li>Ignorance of consumers</li> | ||
<li> | <li>Dishonesty of middlemen</li> | ||
<li>Inadequate market</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Mr. Idowu needs a television and a refrigerator. Each costs N500.00, the exact amount he has. If Mr. Idowu buys the television, the refrigerator would be regarded as the | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>marginal cost</li> | ||
<li> | <li>inferior item</li> | ||
<li> | <li>opportunity cost</li> | ||
<li> | <li>supplementary item</li> | ||
<li>prime cost</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Petro-chemical industries are located in Rivers State of Nigeria due to the presence of | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>a favourable climate</li> | ||
<li> | <li>coal deposits</li> | ||
<li> | <li>oil palm products</li> | ||
<li> | <li>an undulating terrain</li> | ||
<li>oil deposits</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Foreign exchange control in Nigeria is enforced by the | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>commercial banks</li> | ||
<li> | <li>merchant banks</li> | ||
<li> | <li>mortgage banks</li> | ||
<li> | <li>Central Bank</li> | ||
<li>Agricultural Development Bank</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>The difference between the number of immigrants and emigrants is | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>internal mobility</li> | ||
<li> | <li>internal migration</li> | ||
<li> | <li>net migration</li> | ||
<li> | <li>marginal migration</li> | ||
<li>external migration</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Risk-bearing and managerial control are the main functions of the | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>managing director</li> | ||
<li> | <li>manager</li> | ||
<li> | <li>entrepreneur</li> | ||
<li> | <li>chief executive</li> | ||
<li>chief accountant</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>In the table below, the marginal cost when output is 2 units is | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>N16.00</li> | ||
<li> | <li>N20.00</li> | ||
<li> | <li>N36.00</li> | ||
<li> | <li>N40.00</li> | ||
<li>48.00</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>If successive units of labour are added to a piece of land while capital and technology remain constant, a point will be reached in the level of production when each additional unit of labour will add less to the output than previous units. This concept is known as the | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>productivity of labour</li> | ||
<li> | <li>law of diminishing marginal utility</li> | ||
<li> | <li>law of diminishing returns</li> | ||
<li> | <li>law of diminishing returns of a variable factor</li> | ||
<li>internal economies of scale</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Which of the following pairs gives the values of X and Y in the table? | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>X = 20, Y = 6</li> | ||
<li> | <li>X = 10, Y = 10</li> | ||
<li> | <li>X = 38, Y = 9</li> | ||
<li> | <li>X = 46, Y = 9</li> | ||
<li>X = 46, Y = 14</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>When a firm's total revenue is at the maximum, marginal revenue is | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>at the maximum</li> | ||
<li> | <li>negative</li> | ||
<li> | <li>zero</li> | ||
<li> | <li>positive</li> | ||
<li>constant</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Under normal circumstance, a producer will bear the entire burden of taxation on his output if the | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>supply of his goods is more elastic than the demand</li> | ||
<li> | <li>demand for his product is completely elastic</li> | ||
<li> | <li>production of his commodities is subject to diminishing returns</li> | ||
<li> | <li>demand for his product is more elastic than the supply</li> | ||
<li>demand for his product is completely inelastic</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Limited liability means that | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>the debts of a company can only be paid from its own assets</li> | ||
<li> | <li>the debts of a company are paid from business as well as private funds of the owners</li> | ||
<li> | <li>a company does not have to pay its debts</li> | ||
<li> | <li>the debts of a company must be paid from private funds only</li> | ||
<li>government cannot tax a company</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Factory buildings, machinery and raw materials are known in Economics as | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>personal wealth</li> | ||
<li> | <li>social wealth</li> | ||
<li> | <li>government wealth</li> | ||
<li> | <li>business wealth</li> | ||
<li>public wealth</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Abstention from consumption enables capital to be produced. Such abstention is called | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>saving</li> | ||
<li> | <li>Production</li> | ||
<li> | <li>accumulation</li> | ||
<li> | <li>Factors of production</li> | ||
<li>opportunity cost</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Tax evasion in Economics means | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>false declaration of assets</li> | ||
<li> | <li>paying tax only as and when due</li> | ||
<li> | <li>declaration of assets</li> | ||
<li> | <li>tax-payment according to income received</li> | ||
<li>quarrelling with tax collectors</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>The magnitude of the national income of a country depends on all the following except the | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>quantity of natural resources available</li> | ||
<li> | <li>level of technical know-how</li> | ||
<li> | <li>mobility of labour</li> | ||
<li> | <li>level of productivity</li> | ||
<li>quality and quantity of factors of production</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>The Quantity Theory of Money states that an increase in the quantity of money would bring about | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>a geometrical rise in prices</li> | ||
<li> | <li>an unequal rise in prices</li> | ||
<li> | <li>a proportionate rise in prices</li> | ||
<li> | <li>an absolute rise in prices</li> | ||
<li>a less than proportionate increase in prices</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Under the ECOWAS agreement, a Nigerian can enter and stay in Ghana without a visa for a period of | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>14 days</li> | ||
<li> | <li>30 days</li> | ||
<li> | <li>60 days</li> | ||
<li> | <li>90 days</li> | ||
<li>100 days</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
| Line 329: | Line 367: | ||
'''Answer one question only from this section.''' | '''Answer one question only from this section.''' | ||
<ol> | <ol> | ||
<li> | <li><ol type="a"> | ||
<li>What is meant by price elasticity of demand? </li> | |||
<li> | <li>The following figures are extracted from a schedule of demand and supply: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|- | |||
! Price !! Quantity demanded !! Quantity supplied | |||
|- | |||
| N9.00 || 1,050 || 850 | |||
|- | |||
| N10.00 || 1,000 || 1,000 | |||
< | |- | ||
| N11.00 || 950 || 1,150 | |||
|} | |||
<ol type="i"> | <ol type="i"> | ||
<li> | <li>Calculate the elasticity of demand when price rises from N10.00 to N11.00.</li> | ||
<li>State whether the demand in (i) above is elastic or inelastic.</li> | |||
<li>Calculate the elasticity of supply when price falls from N10.00 to N9.00.</li> | |||
<li>State whether the demand in (iii) above is elastic or inelastic.</li> </ol> | |||
</li> </ol> | |||
<li> | |||
<li> | |||
<li> | |||
</li> | |||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Use the data in the table below to answer the questions that follow. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|- | |||
! rowspan="2" | Age group !! colspan="2" | No of persons in thousands | |||
|- | |||
| 1955 || 1960 | |||
|- | |||
| 0 - 16 || 150 || 143 | |||
|- | |||
| 17 - 45 || 51 || 107 | |||
|- | |||
|46 - 60 | |||
|29 | |||
|33 | |||
|- | |||
|above 60 | |||
|15 | |||
|17 | |||
|} | |||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>What is the percentage increase in the working population between 1955 and 1960? </li> | ||
<li>Calculate the ratio of dependent population to the working population in 1955. </li> | |||
<li>Calculate the ratio of dependent population to the working population in 1960. </li> | |||
<li>Has the dependency ratio increased or decreased between 1955 and 1960? </li> </ol> | |||
<li> | |||
<li> | |||
<li> | |||
</li> | </li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
==== Section B ==== | ==== Section B ==== | ||
| Line 451: | Line 419: | ||
<ol start=3> | <ol start=3> | ||
<li> | <li>"Price tends towards the level which equates supply with demand". Explain this statement. </li> | ||
<li>Highlight the economic problems associated with the dependency of West African countries on primary production. </li> | |||
<li><ol type="a"> | |||
<li>Explain the term national debt. </li> | |||
<li>State any four instruments of government borrowing in Nigeria. </li> </ol> | |||
<li> | |||
< | |||
<li> | |||
< | |||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Compare and contrast the private limited company with the public limited company. </li> | ||
<li><ol type="a"> | |||
<li>Outline the main features of the Malthusian theory on population. </li> | |||
<li>Explain the developments that render the theory irrelevant to the present day situation. </li> </ol> | |||
<li> | |||
< | |||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>What is money? Explain its characteristics. </li> | ||
<li><ol type="a"> | |||
<li>Explain the term capital market. </li> | |||
<li>How is the capital market different from the stock exchange? </li> | |||
<li>What are the advantages of the capital market? </li> </ol> | |||
<li> | |||
< | |||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li>Describe the functions of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) </li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
[[Category:WAEC Economics]] | [[Category:WAEC Economics]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:57, 8 May 2025
Economics 1 - Objective
- The definition of Economics as 'the science which studies human behaviour as a relationship between ends and scarce means which have alternative uses' was given by
- Adam Smith
- David Ricardo
- Lionel Robbins
- Thomas R. Malthus
- Robert Giffen
- The concept of economic efficiency primarily implies
- obtaining the maximum output from available resources at the lowest possible cost
- conserving our petroleum resources
- equity in the distribution of the nation's wealth
- producing without waste
- the limited wants-unlimited resources dilemma
- Which of the following is true of NEPA as a public corporation in Nigeria? It is
- a solar energy distributor
- organized in a perfectly competitive market
- a duopoly
- a monopolistically competitive industry
- a monopoly
- A situation of full employment exists when
- every adult is employed
- all adults who can work are employed
- all persons who have attained the age of 15 years and above are employed
- only the disabled are not employed
- all those who are able and eligible to work are employed
- Which of the following functions of money makes it possible for any person to provide for old age
- Medium of exchange
- Store of value
- Measure of value
- Unit of account
- Standard for deferred payments
- The primary objective of the Agricultural Credit Guarantee Scheme is the provision of
- guarantee for loans granted by banks for agricultural purposes
- agricultural inputs to facilitate credit from banks
- loans for every farmer
- agricultural products for farmers
- Which of the following is not an advantage of localization of industries?
- Enjoyment of external economies
- Development of subsidiary industries
- Development of organized markets
- Growth of conurbation
- Which of the following is not an advantage of government ownership of enterprises?
- More capital is provided
- Pricing policy may be in the interest of consumers
- Government workers may be indifferent towards the public
- Infrastructures are rapidly developed
- Income may be more evenly distributed
- If the foreign exchange rate is N8 to £1, then a bicycle bought for £40 will cost
- N15.00
- N60.00
- N100.00
- N250.00
- N320.00
- All the following are assets of a commercial bank except
- cash
- bills discounted
- bank deposits
- investment
- advances to customers
- The Central Bank controls commercial banks through all the following measures except
- the use of directives
- the use of bank rate
- Open market operations
- accepting deposits
- demanding special deposits
- If a person supplements his current income by drawing on past savings in order to make both ends meet, he is said to be living
- a good life
- an average life
- on his savings
- a reckless life
- on borrowed money
- Which of the following is not a set of measures of central tendency?
- Mode and median
- Mean and median
- Mean and mode
- Median and percentage
- Mode, mean and median
- The diagram here is a
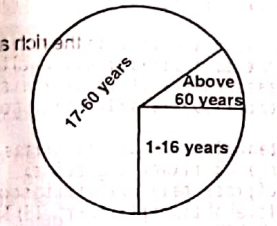
Pie chart - bar chart
- pie chart
- ball chart
- histogram
- histo-chart
- Which of the following pairs can be referred to as middlemen?
- Wholesalers and agents
- Retailers and consumers
- Consumers and agents
- Wholesalers and retailers
- Wholesalers and consumers
- Mono-product economies are those that
- have a rich cultural heritage
- produce only raw materials
- live on the exportation of their raw products
- produce one main commodity
- specialize in agricultural industries
- In diagram below, the broken line labelled PM is the Marginal Revenue Curve of a
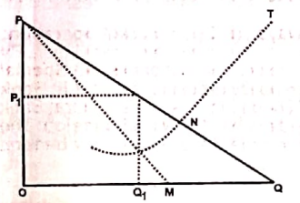
Economics 1994 graph - monopoly
- competitive firm
- state corporation
- partnership
- monopsony
- A Nigerian household's demand curve for semovita is downward sloping because
- the demand for semovita is high
- the local markets are flooded with semovita
- semovita is produced in Nigeria
- every household can afford to buy semovita
- the higher the price of semovita, the lower the quantity demanded
- To the economist, a stock of goods existing at a particular time and conforming to certain requirements such as having utility, money value and being limited in supply, is known as
- consumer goods
- products
- wealth
- commercial goods
- durable goods
- The decision to consume more of one product will under normal circumstance imply that
- more of another product will be consumed
- less of something else will be consumed
- no other product will be consumed
- decision-making is basic in Economics
- enough resources are available
- The difference between the Gross Domestic Product(GDP) and the Gross National Product (GNP) is the
- allowance for total depreciation
- total interest payment
- net income from abroad
- total tax and interest payments
- net internally generated income
- One of the functions of a commercial bank is that it
- is responsible for formulating monetary policies
- accepts demand and time deposits from customers
- is the lender of last resort
- is the banker of the government
- is responsible for issuing currency notes
- Which of the following is not a problem of distribution of goods in Nigeria?
- Poor communication network
- Inadequate storage facilities
- Ignorance of consumers
- Dishonesty of middlemen
- Inadequate market
- Mr. Idowu needs a television and a refrigerator. Each costs N500.00, the exact amount he has. If Mr. Idowu buys the television, the refrigerator would be regarded as the
- marginal cost
- inferior item
- opportunity cost
- supplementary item
- prime cost
- Petro-chemical industries are located in Rivers State of Nigeria due to the presence of
- a favourable climate
- coal deposits
- oil palm products
- an undulating terrain
- oil deposits
- Foreign exchange control in Nigeria is enforced by the
- commercial banks
- merchant banks
- mortgage banks
- Central Bank
- Agricultural Development Bank
- The difference between the number of immigrants and emigrants is
- internal mobility
- internal migration
- net migration
- marginal migration
- external migration
- Risk-bearing and managerial control are the main functions of the
- managing director
- manager
- entrepreneur
- chief executive
- chief accountant
- In the table below, the marginal cost when output is 2 units is
- N16.00
- N20.00
- N36.00
- N40.00
- 48.00
- If successive units of labour are added to a piece of land while capital and technology remain constant, a point will be reached in the level of production when each additional unit of labour will add less to the output than previous units. This concept is known as the
- productivity of labour
- law of diminishing marginal utility
- law of diminishing returns
- law of diminishing returns of a variable factor
- internal economies of scale
- Which of the following pairs gives the values of X and Y in the table?
- X = 20, Y = 6
- X = 10, Y = 10
- X = 38, Y = 9
- X = 46, Y = 9
- X = 46, Y = 14
- When a firm's total revenue is at the maximum, marginal revenue is
- at the maximum
- negative
- zero
- positive
- constant
- Under normal circumstance, a producer will bear the entire burden of taxation on his output if the
- supply of his goods is more elastic than the demand
- demand for his product is completely elastic
- production of his commodities is subject to diminishing returns
- demand for his product is more elastic than the supply
- demand for his product is completely inelastic
- Limited liability means that
- the debts of a company can only be paid from its own assets
- the debts of a company are paid from business as well as private funds of the owners
- a company does not have to pay its debts
- the debts of a company must be paid from private funds only
- government cannot tax a company
- Factory buildings, machinery and raw materials are known in Economics as
- personal wealth
- social wealth
- government wealth
- business wealth
- public wealth
- Abstention from consumption enables capital to be produced. Such abstention is called
- saving
- Production
- accumulation
- Factors of production
- opportunity cost
- Tax evasion in Economics means
- false declaration of assets
- paying tax only as and when due
- declaration of assets
- tax-payment according to income received
- quarrelling with tax collectors
- The magnitude of the national income of a country depends on all the following except the
- quantity of natural resources available
- level of technical know-how
- mobility of labour
- level of productivity
- quality and quantity of factors of production
- The Quantity Theory of Money states that an increase in the quantity of money would bring about
- a geometrical rise in prices
- an unequal rise in prices
- a proportionate rise in prices
- an absolute rise in prices
- a less than proportionate increase in prices
- Under the ECOWAS agreement, a Nigerian can enter and stay in Ghana without a visa for a period of
- 14 days
- 30 days
- 60 days
- 90 days
- 100 days
Economics 2 - Essay
Section A
Answer one question only from this section.
- What is meant by price elasticity of demand?
- The following figures are extracted from a schedule of demand and supply:
Price Quantity demanded Quantity supplied N9.00 1,050 850 N10.00 1,000 1,000 N11.00 950 1,150 - Calculate the elasticity of demand when price rises from N10.00 to N11.00.
- State whether the demand in (i) above is elastic or inelastic.
- Calculate the elasticity of supply when price falls from N10.00 to N9.00.
- State whether the demand in (iii) above is elastic or inelastic.
- Use the data in the table below to answer the questions that follow.
Age group No of persons in thousands 1955 1960 0 - 16 150 143 17 - 45 51 107 46 - 60 29 33 above 60 15 17 - What is the percentage increase in the working population between 1955 and 1960?
- Calculate the ratio of dependent population to the working population in 1955.
- Calculate the ratio of dependent population to the working population in 1960.
- Has the dependency ratio increased or decreased between 1955 and 1960?
Section B
Answer three questions only from this section.
- "Price tends towards the level which equates supply with demand". Explain this statement.
- Highlight the economic problems associated with the dependency of West African countries on primary production.
- Explain the term national debt.
- State any four instruments of government borrowing in Nigeria.
- Compare and contrast the private limited company with the public limited company.
- Outline the main features of the Malthusian theory on population.
- Explain the developments that render the theory irrelevant to the present day situation.
- What is money? Explain its characteristics.
- Explain the term capital market.
- How is the capital market different from the stock exchange?
- What are the advantages of the capital market?
- Describe the functions of the International Monetary Fund (IMF)