2019 Economics WAEC SSCE (School Candidates) May/June: Difference between revisions
(1-27) |
(Added Welcome & Disclaimer Template) |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ | {{Template:PaperIncomplete}} | ||
{{Questions Welcome & Disclaimer|Name=WAEC Economics 2019 May/June paper|ImageName=waec_wikiquestions.png}} | |||
=== Economics 1 - Objective === | === Economics 1 - Objective === | ||
| Line 50: | Line 51: | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li><ol type="a"> | <li>If the demand function is Qd = — 0.5''p'' + 20, calculate the quantity demanded when price is $ 15.00 <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>-$ 27.50 </li> | ||
<li> | <li>-$ 12.50 </li> | ||
<li> | <li>$ 12.50 </li> | ||
<li> | <li>$ 27.50 </li> </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li>The interest rate to control the money supply is a | <li>The interest rate to control the money supply is a | ||
| Line 113: | Line 113: | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li>Table 1 above illustrates the law of | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ Table 1 | |||
|- | |||
! Units of | |||
quantity consumed | |||
! Total Utility !! Marginal Utility | |||
|- | |||
| 0 || _ || _ | |||
|- | |||
| 1 || 10 || 10 | |||
|- | |||
| 2 || 15 || 5 | |||
|- | |||
| 3 || 17 || 2 | |||
|- | |||
| 4 || 18 || 1 | |||
|- | |||
| 5 || 18 || 0 | |||
|} | |||
<li>Table 1 above illustrates the law of | |||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li>diminishing returns </li> | <li>diminishing returns </li> | ||
| Line 152: | Line 171: | ||
<li>variable factors cannot be changed </li> | <li>variable factors cannot be changed </li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li>Table II shows the short-run cost of a firm. Use it to answer question 20. | ||
<li> | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|+ Table II | |||
|- | |||
! Quantity | |||
(kg) | |||
! Fixed | |||
costs($) | |||
! Variable | |||
cost($) | |||
! Total cost | |||
($) | |||
|Marginal | |||
cost($) | |||
|Average | |||
cost($) | |||
|- | |||
| 1 || 750 || 200 || 950 || _ || 950 | |||
|- | |||
| 2 || 750 || 560 || 1310 || 360 || 655 | |||
|- | |||
| 3 || 750 || 900 || '''P'''|| '''Q'''|| 550 | |||
|} | |||
<li>Calculate the value of '''Q''' | |||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>$350</li> | ||
<li> | <li>$340</li> | ||
<li> | <li>$360</li> | ||
<li> | <li>$370</li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
| Line 211: | Line 253: | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li>banks give more loans to businessmen </li> | <li>banks give more loans to businessmen </li> | ||
<li> | <li>large family sizes are encouraged </li> | ||
<li> | <li>general education and training is encouraged. </li> | ||
<li> | <li>It is handled by the private sector only. </li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Agricultural productivity may be increased if | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>educational institutions are established in rural areas </li> | ||
<li> | <li>commercial banks are established in rural areas </li> | ||
<li> | <li>more infrastructural facilities are provided in rural areas </li> | ||
<li> | <li>intensive method of agriculture is encouraged</li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>A country is described as industrialized if | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>the contributions of industries to national income is high</li> | ||
<li> | <li>traditional and modern sectors coexist</li> | ||
<li> | <li>the country adopts import promotion strategy</li> | ||
<li> | <li>primary industries dominate the economy </li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Which of the following is a major advantage of establishing tomato-processing factory in a country? | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>local consumption will decrease </li> | ||
<li> | <li>more unskilled labour will be employed </li> | ||
<li> | <li>foreign exchange will be conserved </li> | ||
<li> | <li>it will attract more tourists </li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>The total value of goods and services are within the borders of a country is | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>net national product</li> | ||
<li> | <li>net domestic product </li> | ||
<li> | <li>gross domestic product </li> | ||
<li> | <li>gross national product </li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Which of the following items is not considered as a transfer payment? | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>pension pay</li> | ||
<li> | <li>Government subsidy </li> | ||
<li> | <li>students grants </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Doctor’s salary </li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Which of the following factors will not underestimate the national income? | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>rapid decrease in prices </li> | ||
<li> | <li>increased subsistence production </li> | ||
<li> | <li>practice of specialization of labour</li> | ||
<li> | <li>increase in value of services not paid for</li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Which of the following is true of the value of money? It | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>is positively related to the price level </li> | ||
<li> | <li>depends on the value people attach to it</li><li>is determined by the government</li><li>is inversely related to the price level </li> </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>The motive for holding money to meet unforeseen events is termed | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>precautionary demand </li> | ||
<li> | <li>transactions demand </li> | ||
<li> | <li>liquidity demand </li> | ||
<li> | <li>speculative demand </li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>An increase in the prices of factor inputs may result in | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>demand-pull inflation </li> | ||
<li> | <li>stagflation </li> | ||
<li> | <li>open inflation </li> | ||
<li> | <li>cost-push inflation </li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Insurance companies are similar to commercial banks in that they | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>compensate their customers for losses </li> | ||
<li> | <li>act as lender of last resort </li> | ||
<li> | <li>help in maintaining monetary Stability in a nation</li> | ||
<li> | <li>help in mobilizing savings for investment </li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>What happens when the central bank creases the bank rate? | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>amount of borrowing increases </li> | ||
<li> | <li>amount of borrowing decreases </li> | ||
<li> | <li>supply of money money increases </li> | ||
<li> | <li>commercial banks are not affected </li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Citizens are protected from government's arbitrariness in taxation by the canon of | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>elasticity</li> | ||
<li> | <li>flexibility</li> | ||
<li> | <li>economy </li> | ||
<li> | <li>certainty </li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Period of unemployment and falling prices, governments should adopt a | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>zero-based budget </li> | ||
<li> | <li>budget deficit </li> | ||
<li> | <li>balanced budget</li> | ||
<li> | <li>surplus budget</li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>In most developing countries, a large percentage of the labour force is engaged in | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>trading</li> | ||
<li> | <li>mining</li> | ||
<li> | <li>agriculture</li> | ||
<li> | <li>manufacturing</li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>In most underdeveloped countries, development plans do not achieve their objective due to | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>poor coordination between local and national governments</li> | ||
<li> | <li>exportation of more primary products </li> | ||
<li> | <li>lack of educational institutions in those countries </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Urban-rural migration of citizens </li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Balance of trade involves exchange of | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>goods only</li> | ||
<li> | <li>services only</li> | ||
<li> | <li>goods and services </li> | ||
<li> | <li>good and capital</li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>An improvement in a country’s term of trade means that the | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>nation can export more services </li> | ||
<li> | <li>nation’s receipts on export is equal to payments on imports </li> | ||
<li> | <li>value of her imports is lower than her exports </li> | ||
<li> | <li>visible exports is less than visible imports</li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Devaluation of currency may not correct a balance of payments deficit if the demand for export is | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>perfectly inelastic </li> | ||
<li> | <li>perfectly elastic</li> | ||
<li> | <li>fairly elastic</li> | ||
<li> | <li>unitary elastic </li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>One measure for financing a country’s balance of payments deficit is thorough | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>export diversification</li> | ||
<li> | <li>import substitution </li> | ||
<li> | <li>short term borrowing from IMF </li> | ||
<li> | <li>internal borrowing from commercial banks </li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>The major achievement of the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) is that it has | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>made capital more mobile </li> | ||
<li> | <li>made possible the use of common currency </li> | ||
<li> | <li>increased members allegiance to former colonial masters</li> | ||
<li> | <li>widened the market for goods produced </li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Which of the following institutions is concerned with expanding developing countries’ commodity trade? | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>World Trade Organization (WTO) </li> | ||
<li> | <li>United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Economic Commission for Africa (ECA) </li> | ||
<li> | <li>African Development Bank (AFDB) </li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Exploitation of forest resources becomes a major problem where | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>communities fight over ownership </li> | ||
<li> | <li>they are not renewed </li> | ||
<li> | <li>they are neglected </li> | ||
<li> | <li>the supply is fixed in the long-run </li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Natural resources that are renewable are found in the | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | <li>mining sector</li> | ||
<li> | <li>traditional sector </li> | ||
<li> | <li>agricultural sector </li> | ||
<li> | <li>secondary sector </li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
| Line 406: | Line 445: | ||
'''Answer one question only from this section.''' | '''Answer one question only from this section.''' | ||
<ol> | <ol> | ||
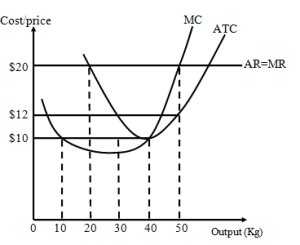
<li> | <li>The diagram below represents the equilibrium position of a firm in a perfectly competitive industry. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow cost/price | ||
<ol type="a"> | <ol type="a"> | ||
<li> | [[File: WA2019_ECONS_P2Q001.png|thumb]] | ||
<li><ol type="i"> | |||
<li> | <li>At what level of output and prices is the firm in equilibrium? </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Calculate the firm’s profit in equilibrium </li> | ||
<li> | <li>What type of profits is it? Explain your answer.</li> </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li><ol type="i"> | ||
<li>Why is the average revenue (AR) function horizontal? </li> </ol> | |||
<li> | |||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>State any two ways in which marginal cost (MC) and average total cost (ATC) are related. </li> </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>The extract from a country’s balance of payments account is shown below. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|+ Caption text | |||
|- | |||
! ITEM !! IMPORT | |||
($ million ) | |||
! EXPORT | |||
($ million ) | |||
|- | |||
| Agricultural | |||
products | |||
| _ || 200 | |||
|- | |||
| Mineral products || _ || 300 | |||
|- | |||
| Consumer goods || 250 || _ | |||
|- | |||
| Capital goods || 400 || _ | |||
|- | |||
| Insurance || 50 || 25 | |||
|- | |||
| Banking || 75 || 30 | |||
|- | |||
| Transportation || 85 || 25 | |||
|- | |||
| Loans || 150 || 60 | |||
|} | |||
<ol type="a"> | |||
Using the table above, calculate the | |||
<li>balance of trade </li> | |||
<li>invisible trade balance</li> | |||
<li>balance on current account. </li> </ol> | |||
</li> | </li> | ||
</ol> | </ol>'''Answer three questions only from this section.''' | ||
'''Answer three questions only from this section.''' | |||
<ol start=3> | <ol start=3> | ||
<li> | <li><ol type="a"> | ||
<li><ol type="i"> | |||
<li> | <li>Define distribution of goods </li> | ||
<li>illustrate the normal chain or distribution of goods </li> </ol> | |||
<li> | |||
<li> | |||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li>Describe a consumer’s cooperative society </li> | |||
<li>Outline any four roles performed by a consumers’ cooperative society </li> </ol> | |||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li><ol type="a"> | ||
<li>What is an industry? </li> | |||
<li> | <li>Explain the following: | ||
<li> | |||
<ol type="i"> | <ol type="i"> | ||
<li> | <li>Division of labour </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Economies of scale </li> </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li>Outline any four internal economies of scale </li> </ol> | |||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li><ol type="a"> | ||
<li>Define a joint venture </li> | |||
<li> | <li>Identify any three merits of a private company over a partnership </li> | ||
<li>State any three sources of finance to a public enterprise </li> </ol> | |||
< | |||
< | |||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li><ol type="a"> | ||
<li>Distinguish between the following pairs of concept: | |||
<li> | |||
<ol type="i"> | <ol type="i"> | ||
<li> | <li>elastic demand and inelastic demand</li> | ||
<li> | <li>income elasticity of demand and cross elasticity of demand </li> </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Using diagrams, explain how an increase in price will affect the total revenue of a producer if demand for his product is: | ||
<ol type="i"> | <ol type="i"> | ||
<li> | <li>Price elastic </li> | ||
<li> | <li>price inelastic </li> </ol> | ||
</li> </ol> | |||
</li> | |||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li><ol type="a"> | ||
<li>Distinguish between: | |||
<li> | |||
<ol type="i"> | <ol type="i"> | ||
<li> | <li>a growing population and a declining population</li> | ||
<li> | <li>overpopulation and underpopulation </li> </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li>Explain any four disadvantages of a rapidly growing population in an economy. </li> </ol> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li> | <li><ol type="a"> | ||
<li>What is public debt? </li> | |||
<li> | <li>Outline any three reasons why countries borrow </li> | ||
<li>Highlight any three effects of a huge national debt on the economy of a country. </li> </ol> | |||
<li> | |||
< | |||
</li> | </li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
[[Category:WAEC Economics]] | [[Category:WAEC Economics]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:14, 9 September 2024
![]() Some elements of this question paper are missing.
Some elements of this question paper are missing.
If you have a complete version of this question paper, you can send us an email.

Today, we're excited to share the WAEC Economics 2019 May/June paper. This is WikiQuestions.org, your ultimate destination for free past exam papers. We aim to help you excel in your studies by offering accurate and reliable resources. We are committed to providing students access to a comprehensive collection of past papers to support their exam preparation.
Disclaimer
At WikiQuestions.org, we strive to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the exam papers we provide. However, neither WikiQuestions.org, its parent organization, nor any of the volunteer contributors can be held liable for any errors, omissions, or inaccuracies in the content. Users are encouraged to verify the information with official sources. We are in no way affiliated with the examining body; the questions have been contributed and maintained by various volunteers.
Economics 1 - Objective
- The fundamental economic problem in every society is
- the large number of the unemployed
- inadequate supply of money
- corruption and mismanagement
- limited supply of productive resources
- A point X inside a production possibility curve indicates that
- resources are fully utilized
- the country is poor
- some resources are idle
- resources are not available
- The major employer of labour in developing countries is the
- tertiary sector
- secondary sector
- primary sector
- industrial sector
- The desire for profit is a major feature of
- traditional economy
- mixed economy
- market economy
- command economy
- The wages of a group of workers in dollars are stated below: 40, 30, 70, 20, 60, 10, 10, 80, 30 and 10. What is the mean wage?
- $35
- $36
- $37
- $38
- If the coefficient of price elasticity of demand of a product is zero, then its demand curve will be
- parallel to the quantity axis
- parallel to the price axis
- negatively sloped
- positively sloped
- If the demand function is Qd = — 0.5p + 20, calculate the quantity demanded when price is $ 15.00
- -$ 27.50
- -$ 12.50
- $ 12.50
- $ 27.50
- The interest rate to control the money supply is a
- control policy
- monetary policy
- developmental policy
- fiscal policy
- If less of a good is bought as one’s in- come increases, such good is
- a normal good
- a luxury
- a necessity
- an inferior good
- The demand for coffee and tea is
- joint
- competitive
- composite
- derived
- What effect will an increase in the supply of fish have on the meat market?
- a fall in equilibrium price and quantity
- An increase in equilibrium price and quantity
- an increase in equilibrium price and quantity
- Both equilibrium price and quantity remain unchanged
- Which of the following factors is not a condition for a charge in supply of a commodity?
- improved technology
- cost of production
- the price of the commodity
- Government tax policies
- Supply of agricultural product is likely to be elastic in the
- intermediate period
- long run
- market period
- short-run
- Two commodities X and Y are in joint supply when
- X is a by product of Y
- X and Y are produced by the same firm
- increase in quantity of X leads to decrease in Y
- X and Y cannot be produced in the same process
- Table 1 above illustrates the law of
- diminishing returns
- diminishing marginal productivity
- diminishing marginal utility
- variable proportion
- When the price of a good is above the equilibrium, there will be
- a shortage
- a surplus
- unemployment
- inflation
- What happens when a minimum price is imposed in a market?
- shortage occurs
- surplus occurs
- the market maintains its equilibrium
- Many firms will close down
- When an increase in inputs leads to more than a proportionate increase in output, there is
- decreasing returns to scale
- increase in marginal product
- increasing returns to scale
- constant returns to scale
- The short-run in production is the time period when
- techniques of production can easily be changed
- all factors of production are variable
- at least a factor is fixed while others are variable
- variable factors cannot be changed
Table II shows the short-run cost of a firm. Use it to answer question 20.
- Calculate the value of Q
- $350
- $340
- $360
- $370
- A cost of production that is positively related to output is the
- total fixed cost
- average fixed cost
- variable cost
- social cost
- In perfect competition, the average revenue curve of a firm
- below the marginal revenue curve
- downward sloping
- the marginal revenue curve
- convex to the origin
- Which of the following means of funding a business is a very reliable and cheap?
- Bank loans
- Loans from friends
- Plough back profits
- Debentures
- Government in most cases influences location of a firm to
- discourage private investors
- ensure equitable distribution
- reduce cost of production
- make the firms enjoy economies of scale
- Middlemen are made up of
- manufacturers, wholesalers and consumer
- manufacturers, wholesalers and retailers
- wholesalers, retailers and hawkers
- wholesalers, retailers and consumers
- The Malthusian theory of population was proved wrong because
- the practice of subsistence farming was encouraged
- developing countries adopted birth control method
- new lands and new methods of production were discovered
- Malthus’ view was seen as an exaggeration
- Human development can be improved if
- banks give more loans to businessmen
- large family sizes are encouraged
- general education and training is encouraged.
- It is handled by the private sector only.
- Agricultural productivity may be increased if
- educational institutions are established in rural areas
- commercial banks are established in rural areas
- more infrastructural facilities are provided in rural areas
- intensive method of agriculture is encouraged
- A country is described as industrialized if
- the contributions of industries to national income is high
- traditional and modern sectors coexist
- the country adopts import promotion strategy
- primary industries dominate the economy
- Which of the following is a major advantage of establishing tomato-processing factory in a country?
- local consumption will decrease
- more unskilled labour will be employed
- foreign exchange will be conserved
- it will attract more tourists
- The total value of goods and services are within the borders of a country is
- net national product
- net domestic product
- gross domestic product
- gross national product
- Which of the following items is not considered as a transfer payment?
- pension pay
- Government subsidy
- students grants
- Doctor’s salary
- Which of the following factors will not underestimate the national income?
- rapid decrease in prices
- increased subsistence production
- practice of specialization of labour
- increase in value of services not paid for
- Which of the following is true of the value of money? It
- is positively related to the price level
- depends on the value people attach to it
- is determined by the government
- is inversely related to the price level
- The motive for holding money to meet unforeseen events is termed
- precautionary demand
- transactions demand
- liquidity demand
- speculative demand
- An increase in the prices of factor inputs may result in
- demand-pull inflation
- stagflation
- open inflation
- cost-push inflation
- Insurance companies are similar to commercial banks in that they
- compensate their customers for losses
- act as lender of last resort
- help in maintaining monetary Stability in a nation
- help in mobilizing savings for investment
- What happens when the central bank creases the bank rate?
- amount of borrowing increases
- amount of borrowing decreases
- supply of money money increases
- commercial banks are not affected
- Citizens are protected from government's arbitrariness in taxation by the canon of
- elasticity
- flexibility
- economy
- certainty
- Period of unemployment and falling prices, governments should adopt a
- zero-based budget
- budget deficit
- balanced budget
- surplus budget
- In most developing countries, a large percentage of the labour force is engaged in
- trading
- mining
- agriculture
- manufacturing
- In most underdeveloped countries, development plans do not achieve their objective due to
- poor coordination between local and national governments
- exportation of more primary products
- lack of educational institutions in those countries
- Urban-rural migration of citizens
- Balance of trade involves exchange of
- goods only
- services only
- goods and services
- good and capital
- An improvement in a country’s term of trade means that the
- nation can export more services
- nation’s receipts on export is equal to payments on imports
- value of her imports is lower than her exports
- visible exports is less than visible imports
- Devaluation of currency may not correct a balance of payments deficit if the demand for export is
- perfectly inelastic
- perfectly elastic
- fairly elastic
- unitary elastic
- One measure for financing a country’s balance of payments deficit is thorough
- export diversification
- import substitution
- short term borrowing from IMF
- internal borrowing from commercial banks
- The major achievement of the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) is that it has
- made capital more mobile
- made possible the use of common currency
- increased members allegiance to former colonial masters
- widened the market for goods produced
- Which of the following institutions is concerned with expanding developing countries’ commodity trade?
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD)
- Economic Commission for Africa (ECA)
- African Development Bank (AFDB)
- Exploitation of forest resources becomes a major problem where
- communities fight over ownership
- they are not renewed
- they are neglected
- the supply is fixed in the long-run
- Natural resources that are renewable are found in the
- mining sector
- traditional sector
- agricultural sector
- secondary sector
| Units of
quantity consumed |
Total Utility | Marginal Utility |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | _ | _ |
| 1 | 10 | 10 |
| 2 | 15 | 5 |
| 3 | 17 | 2 |
| 4 | 18 | 1 |
| 5 | 18 | 0 |
| Quantity
(kg) |
Fixed
costs($) |
Variable
cost($) |
Total cost
($) |
Marginal
cost($) |
Average
cost($) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 750 | 200 | 950 | _ | 950 |
| 2 | 750 | 560 | 1310 | 360 | 655 |
| 3 | 750 | 900 | P | Q | 550 |
Economics 2 - Essay
Section A
Answer one question only from this section.
- The diagram below represents the equilibrium position of a firm in a perfectly competitive industry. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow cost/price
- The extract from a country’s balance of payments account is shown below.
Caption text ITEM IMPORT ($ million )
EXPORT ($ million )
Agricultural products
_ 200 Mineral products _ 300 Consumer goods 250 _ Capital goods 400 _ Insurance 50 25 Banking 75 30 Transportation 85 25 Loans 150 60 -
Using the table above, calculate the
- balance of trade
- invisible trade balance
- balance on current account.
Answer three questions only from this section.
- Define distribution of goods
- illustrate the normal chain or distribution of goods
- Describe a consumer’s cooperative society
- Outline any four roles performed by a consumers’ cooperative society
- What is an industry?
- Explain the following:
- Division of labour
- Economies of scale
- Outline any four internal economies of scale
- Define a joint venture
- Identify any three merits of a private company over a partnership
- State any three sources of finance to a public enterprise
- Distinguish between the following pairs of concept:
- elastic demand and inelastic demand
- income elasticity of demand and cross elasticity of demand
- Using diagrams, explain how an increase in price will affect the total revenue of a producer if demand for his product is:
- Price elastic
- price inelastic
- Distinguish between the following pairs of concept:
- Distinguish between:
- a growing population and a declining population
- overpopulation and underpopulation
- Explain any four disadvantages of a rapidly growing population in an economy.
- Distinguish between:
- What is public debt?
- Outline any three reasons why countries borrow
- Highlight any three effects of a huge national debt on the economy of a country.